| 方法 | 说明 |
| void setPriority(int newPriority) | 更改线程优先级 |
| static void sleep(long millis) | 让正在执行的线程休眠 |
| void join() | (插队)等待该线程终止 |
| static void yield() | (礼让)暂停正在执行的线程对象,并执行其他线程 |
| void interrupt() | 中断线程,别用这个方式 |
| boolean isAlive() | 判断线程是否处于活动状态(就绪或运行) |
线程停止
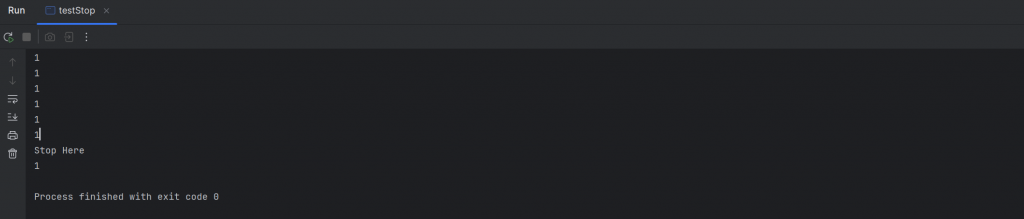
线程停止的方法:设置一个标志位flag,例如:
public class testStop implements Runnable{
static boolean flag = true;
public static void stop(){
flag=false;
}
public void run(){
while (flag){
System.out.println(1);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
new Thread(new testStop()).start();
for(int i=0 ; i<100000 ; i++){
if(i==90000){
System.out.println("Stop Here");
stop();
}
}
}
}
线程休眠
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
public class testsleep {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
for(int i=0 ; i<10 ; i++){
Date timenow = new Date(System.currentTimeMillis()); //获取当前系统时间
System.out.println(new SimpleDateFormat("HH:mm:ss").format(timenow));
Thread.sleep(1000); //当前进程休眠1秒
}
}
}线程礼让
public class testYield implements Runnable{
public void run(){
for(int i = 0 ; i<5 ; i++){
System.out.printf("trd = %s ; i = %d\n",Thread.currentThread().getName(),i);
if(i==3){
Thread.yield(); //礼让给另一线程
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
new Thread(new testYield(),"AAA").start();
new Thread(new testYield(),"BBB").start();
}
}

线程强制执行
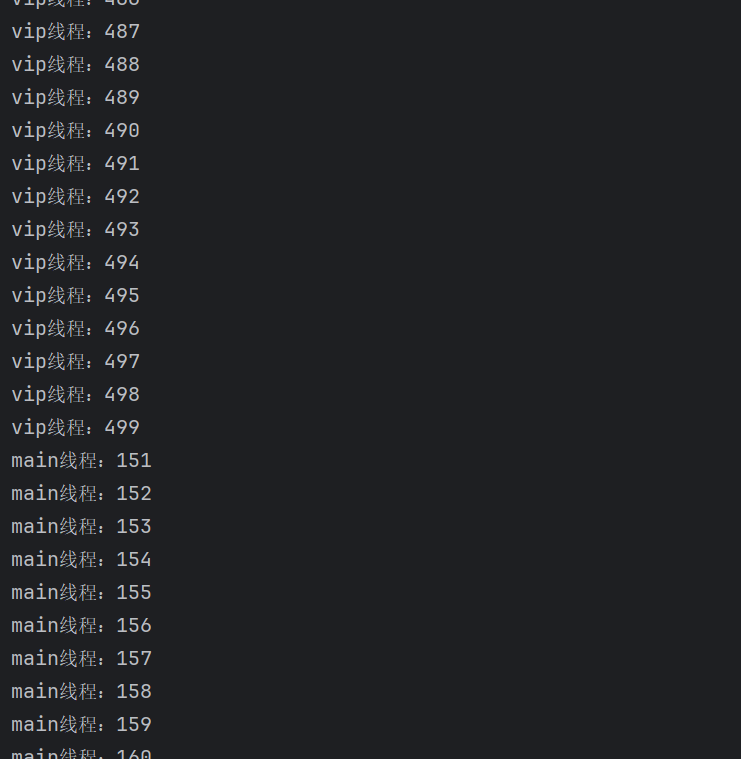
public class testJoin implements Runnable{
public void run(){
for(int i = 0 ; i < 500 ; i++){
System.out.printf("vip线程:%d\n",i);
}
}
public static void main(String[] a) throws InterruptedException {
testJoin testJoin = new testJoin();
Thread thread = new Thread(testJoin);
thread.start();
for(int i = 0 ; i < 500 ; i++){
System.out.printf("main线程:%d\n",i);
if (i == 150){
System.out.println("此处join");
thread.join(); //插队,直到此线程终止
}
}
}
}
观测线程状态
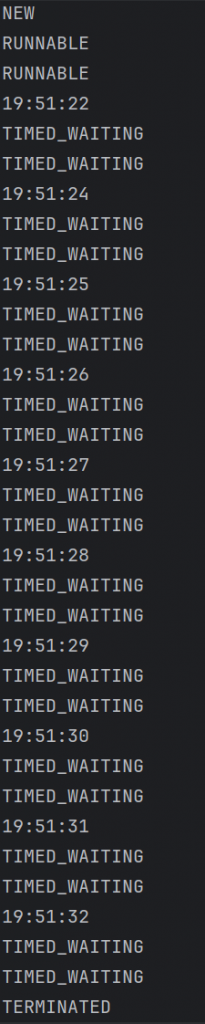
getState返回该线程的状态,状态的代码见官方文档中:

可知NEW是创建状态, RUNNABLE是运行状态, BLOCKED/WAITING/TIMED_WAITING是阻塞状态, TERMINATED是死亡状态。
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.Objects;
public class testState implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
for(int i=0 ; i<10 ; i++){
Date timenow = new Date(System.currentTimeMillis()); //获取当前系统时间
System.out.println(new SimpleDateFormat("HH:mm:ss").format(timenow));
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread thread = new Thread(new testState());
System.out.println(thread.getState()); //NEW(尚未启动)
thread.start();
System.out.println(thread.getState()); //RUNNABLE(运行中)
while (true){
String st = String.valueOf(thread.getState());
System.out.println(st);//TIMED_WAITING(等待sleep(1000)结束)
Thread.sleep(500); //每隔500ms检测一次thread状态
if(st == "TERMINATED"){ //终止
break;
}
}
}
}
线程优先级设置
优先级高的线程更有可能被CPU优先调度执行 最高优先级为10,最低为1
public class testPriority {
public static void main(String a[]){
System.out.println(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY);//10
System.out.println(Thread.MIN_PRIORITY);//1
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"运行了,他的优先级是"+Thread.currentThread().getPriority()); //main线程的默认优先级
p p = new p();
Thread t1 = new Thread(p);
Thread t2 = new Thread(p);
Thread t3 = new Thread(p);
Thread t4 = new Thread(p);
Thread t5 = new Thread(p);
t1.setPriority(4);//设置优先级
t1.start();//启动线程
t2.setPriority(7);
t2.start();
t3.setPriority(2);
t3.start();
t4.setPriority(10);
t4.start();
t5.setPriority(8);
t5.start();
//不一定按照优先级顺序启动,要看CPU是否先调度。
}
}
class p implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"运行了,他的优先级是"+Thread.currentThread().getPriority());
}
}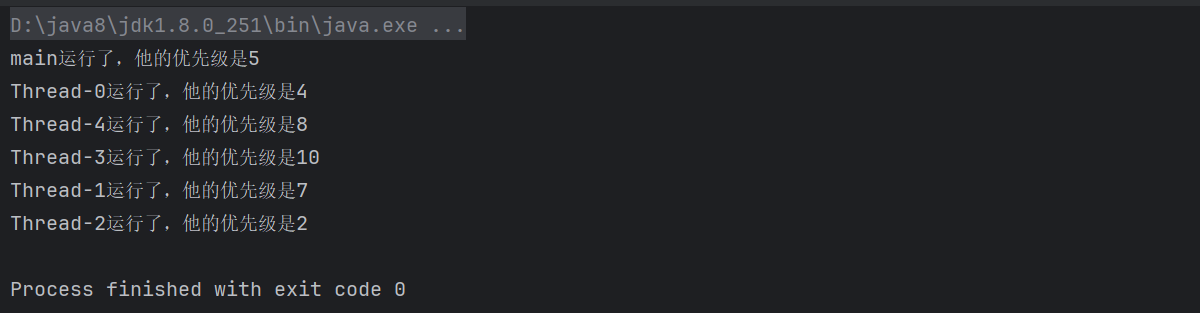 由此可知,优先级高的线程不一定先执行。
由此可知,优先级高的线程不一定先执行。
守护线程
thread = new Thread(new testdeamon());
thread.setDeamon(true)可以将thread线程设置为守护线程。java虚拟机不会等待守护进程结束而结束,即守护线程可以一直运行,直到用户线程全部运行完后,随jvm一起关闭。










Comments NOTHING